testing for tibial torsion|how to measure tibial torsion : maker The diagnosis of tibial torsion is made by a history and physical examination by your child's doctor. During the examination, the doctor obtains a complete prenatal and birth history of the . 23 de dez. de 2022 · A look at the rise and fall of video game leakers in 2022, from the accurate to the fraudulent, and the impact of leaks on the gaming industry and fans. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBContacting Napoleon Games directly? Here you'll find the contact details such as address, email, and phone number.
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn .The diagnosis of tibial torsion is made by a history and physical examination by your child's doctor. During the examination, the doctor obtains a complete prenatal and birth history of the . Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. Males and females are affected equally, .
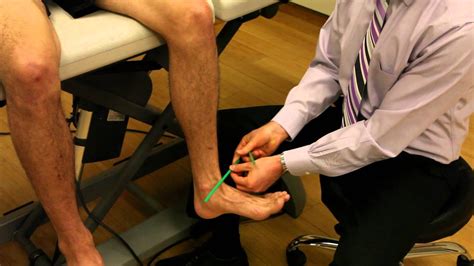
Tibial torsion can be assessed by comparing the bimalleolar axis with the position of the tibial tubercle. Note the foot shape: Metatarsus adductus may be the primary cause of in-toeing, particularly in the infant.To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child prone and the knees flexed to 90°. Typically the foot axis is 10° lateral .
To evaluate for tibial torsion, the angle between the axis of the foot and the axis of the thigh is measured with the child prone and the knees flexed to 90°. Typically the foot axis is 10° lateral .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. This condition causes a child to have inward-facing toes and bowed legs. It may be caused by the position of the baby in the uterus. .
Tibial Torsion - TeachMe Orthopedics Tibial Torsion - TeachMe Orthopedics. Publisher - Learn Orthopedics with Ease. Basic Science. Anatomy; Examination; Trauma. . but this test often is unnecessary because .We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. Males and females are affected equally, and about two thirds of patients are affected bilaterally. [1, 2] Tibial torsion can persist into adulthood and give rise to patellofemoral pathology.
Tibial torsion occurs if the child's lower leg (tibia) twists inward. This can occur before birth, as the legs rotate to fit in the confined (limited) space of the womb. After birth, an infant's legs should gradually rotate to align properly. If the lower leg remains turned in, the result is tibial torsion. trochanteric prominence angle test . . tibial torsion. look at thigh-foot angle in prone position. normal value in infants- mean 5° internal (range, −30° to +20°) normal value at age 8 years- mean 10° external (range, −5° to +30°) metatarsus adductus.Tibial Torsion What is tibial torsion in children? Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child’s feet to turn inward. . At the visit, write down the name of a new diagnosis and any new medicines, treatments, or tests. Also write down any new .
What causes tibial torsion? Tibial torsion tends to be hereditary and can be passed down from parents to children. The position of a fetus in the uterus can also make a child more likely to have tibial torsion. What are the symptoms of tibial torsion? The "in-toeing", or walking with the toes pointed inward, is the primary symptom of tibial .By mid-childhood, a small percentage of children will continue to have significant tibial torsion. How is tibial torsion diagnosed? Tibial torsion is diagnosed (and distinguished from other causes of in-toeing) by a careful physical exam. Tibial torsion is assessed by measuring the thigh-foot angle, if the foot is shaped normally.
Out-toeing is caused by external tibial torsion and femoral retroversion. . rotation with femoral retroversion. 3, 4 Thigh-foot angle testing is positive for tibial torsion when the foot turns .
Physical exam test procedure for examination of the foot and ankle and associated structures. Normally, lateral rotation of the tibia increases from approximately 5º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity; femoral anteversion decreases from approximately 40º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity. Tibial torsion Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of intoeing. Tibial torsion was calculated by subtracting the proximal tibial angle from the distal tibial angle. . The accuracy of a test can be defined as how close a measured value is to a true value. In this case it means, how close the clinical measurement of tibial torsion is to the real torsion measured by CT or in a cadaver. .
tibial torsion special test
Tibial torsions (especially external tibial torsion) are often associated with (1) increased incidence of knee osteoarthritis later in life and (2) increased incidence of osteochondritis dissecans. They can also be a predisposing factor for (3) .
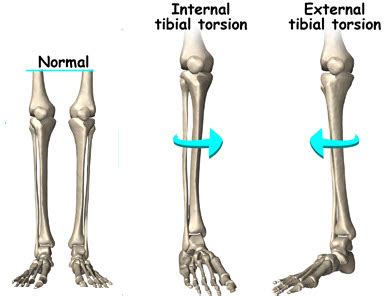
Clinical resource with information about Tibial torsion bilateral medial and its clinical features, available genetic tests from US and labs around the world and links to practice guidelines and authoritative resources like GeneReviews, PubMed, MedlinePlus, . Tibial torsion (twisting of the tibia) can cause toeing in or out, depending on .Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test (TPAT)'. Femoral anteversion is the angle between the femoral neck and femoral shaft, indicating the degree of torsion of the femur. It is also known as Femoral neck anteversion.
The etiology of intoeing (i.e., metatarsus adductus, internal tibial torsion, and increased femoral anteversion) is debated, although the causes generally can be correlated with the patient's age .
Torsión tibial ¿Qué es la torsión tibial? La torsión tibial es una torsión hacia adentro de los huesos de la canilla (los huesos que están entre la rodilla y el tobillo). La torsión tibial hace que los pies del niño apunten hacia adentro. Es por esto que algunos lo llaman "dedos de paloma". Se ve comúnmente en niños que empiezan a . Tibial torsion is a twist in the tibia measured as an angle between a proximal axis line and a distal axis line. Abnormal torsion has been associated with a variety of painful clinical syndromes of the lower limb. . SL, and MRI scans, and between males and females, were compared using t tests. SPSS was used for all statistical analysis. Results:In the measurements using the new method, tibial torsion values at first measurement made by four trained physicians were 35 ± 8.6° (range 16–70°), and for the next month measurements it was 35.2 ± 9.1° (range 6–71.5°) ().Analysis of variance between all measurement sessions with the two techniques of measurement did not show any significant difference, so it can be . These tests are applied by to therapist or doctor in the clinic to check the tibial torsion of the ankle. When testing for tibial torsion, the examiner must realize that some lateral tibial torsion [ 13′ to 18′ in adults, less in children ] is normally present.
External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with Blount disease. Persistent .Look for posterior sag, and apply anterior force if supine or test prone for neutral tibial positioning. Reverse Pivot Shift Test: Original Pivot Shift. Reverse Pivot Shift Test video provided by Clinically Relevant (+) test, knee subluxation in flexion and posterior sag of proximal tibia;
External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically resolves with growth. However, an excessive degree of torsion may indicate a neuromuscular problem. Torsion also occurs with Blount disease. Persistent .
By testing knees at different tibial rotations, it was discovered that at 15° of tibial external rotation above the neutral position, significantly increased average and peak patellofemoral contact pressures were appreciated at all knee flexion angles. . For tibial torsion, the most commonly used examination techniques are the thigh-foot . Electrodiagnostic testing of tibial neuropathy is often technically difficult, particularly in cases of tarsal tunnel syndrome, due to difficulty isolating the distal portions of the tibial nerve. This is particularly evident in older patients. Abnormal EMG findings may be present in the intrinsic muscles of the foot in asymptomatic patients.
tibial torsion in adults
webGuía de casinos de la ciudad de Mexico City: información sobre juegos de azar, horarios de apertura, dejar una reseña sobre casinos de la ciudad Mexico City.
testing for tibial torsion|how to measure tibial torsion